Variable Geometry Turbocharger - Explained
One way that vehicle manufacturers often use to increase engine power in small capacity engines is to use Turbocharger. Yes, the time has proven that a turbocharger can increase engine power to 15% - 25% or more in a small capacity engine.
Along with the development and need for increased engine performance, the Turbocharger also has encountered changes (evolution), one of which is the development of Variable Geometry Turbocharger, often abbreviated as VGT.
The main purpose of using variable Geometry Turbocharger (VGT) technology is similar to Turbocharger, which produces greater engine output power without increasing engine capacity (cc), so the engine power can become more efficient and powerful.
VGT technology has become widely used for vehicles worldwide, such as the Kia Sorento, Kia New Sportage CRDi, Mitsubishi Montero Sport, Mitsubishi Strada, Hyundai Santa Fe, Hyundai H-1, Isuzu Mu-X, and Chevrolet Trailblazer, and many more.
What is a Variable Geometry Turbocharger?
Variable Geometry Turbochargercharger has the same way working of with Turbochargers in general, utilizing the energy generated by exhaust gas to rotate the turbine to increase the supply of fresh air volume into the intake manifold.
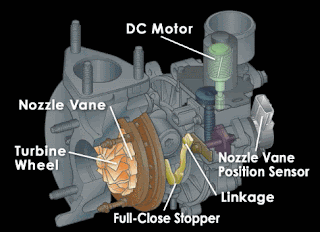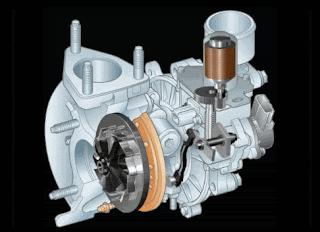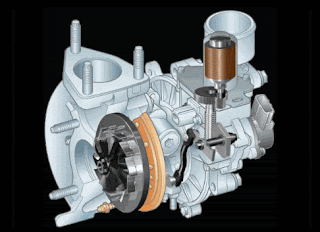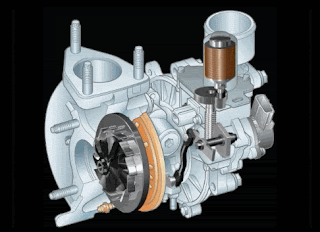
However, the special Turbocharger type VGT is equipped with adjustable fins around the main turbine.
The fins can change their angle according to engine speed to avoid Turbocharger Lag. In addition, changing the angle on the VGT fins will also increase maximum engine performance at low RPM as well as high RPM. In effect, the torque increases at low rpm while at the same time making the use of fuel more efficient.
Read also:Variable Geometry Turbocharge (VGT) working process
Turbocharger with VGT technology is commonly used on engines with Diesel Common Rail system technology. The Variable Geometry Turbocharger uses a DC motor controlled by the engine computer (ECM) to open and close the fins. The ECM plays an important role in executing when the time is right to open or close the Variable Geometry Turbocharger fins.
In general, changes and movements of the Variable Geometry Turbocharger fins occur when switching from low RPM to high RPM or vice versa. Pay attention to the two conditions below.
Low RPM
Please pay close attention to the VGT fins and turbine rotation in the animated image below (low rpm conditions)
When the engine RPM is low to medium, the condition of the fins on the VGT Turbocharger will close slightly. It serves to narrow the passageway in the exhaust gas and direct the flow of exhaust gas power.
The narrower the cavity is created, the more pressure flow in the exhaust gas will also increase. It will cause the turbine to spin faster.
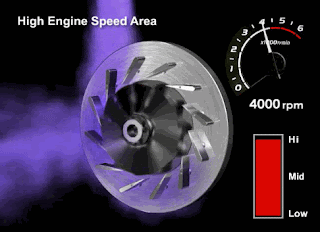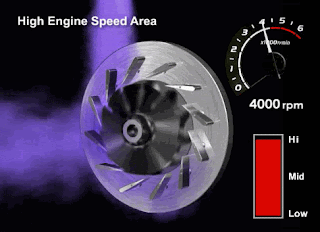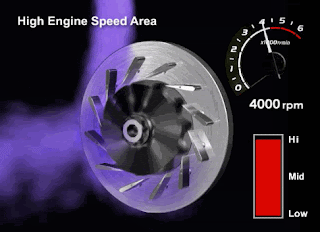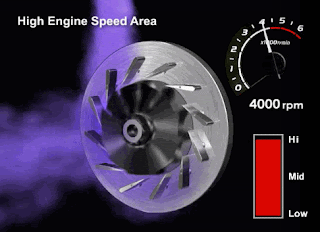
High RPM
Please pay close attention to the VGT fins and turbine rotation in the animated image below (high rpm conditions)
When the engine RPM is at high rotation, the volume and contents of the exhaust gas created will be denser. Therefore, the ECM will instruct the DC Motor to open the VGT fins so the Turbocharger can reduce the exhaust gas back pressure and maintain the turbine rotation speed.