How car cooling system works?
The car engine (internal combustion type) produces heat while it's working. So, to prevent the engine from damage because of the heat, the cooling system was added. There are two types of cooling systems use in a car, air-cooled and liquid-cooled.
Air-cooled means that the engine using airflow to maintain its temperature. While the liquid-cooled is uses a liquid material called coolant or antifreeze to maintain the heat generated by the engine.
Most modern cars use a liquid cooling system. So, in this post, we will give you information on how the cooling system in a car works, mainly with the liquid cooling system. But before that, it's better to know car cooling system parts and function. See the parts and the function of the cooling system in a car on the list of details below.
I. The parts of cooling system in a car
The car cooling system is gathered by several engine components placed inside and outside the engine as a system. The components work together to maintain the engine temperature so that the engine will work efficiently. Below are the main parts of cooling system in a car and its function.
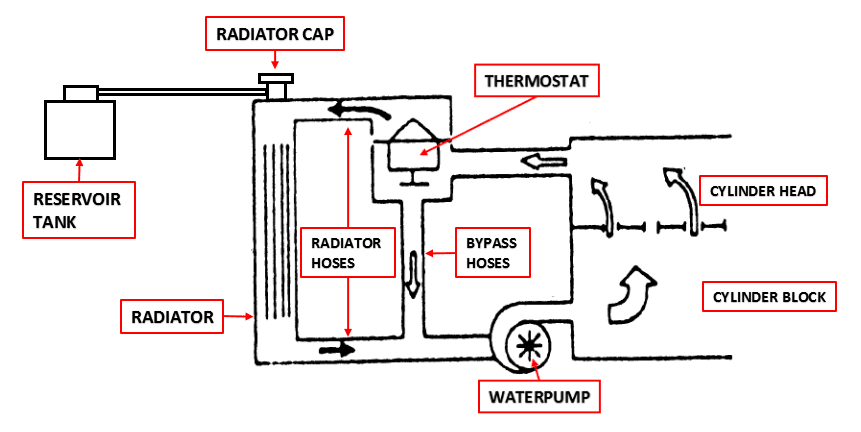
- Radiator; Radiator function is to release the heat from the coolant to the open air. The radiator has additional parts to working properly, such as a radiator cap, reservoir tank, and fan shroud.
- Radiator hoses; Radiator hose's function is to connecting between the radiator and the engine so the coolant can circulate better. There are two radiator hoses, upper hose, and lower hose.
- Radiator fan; Radiator fan function is to create flowing air in the radiator core pipes and fins so the heat can release easily to the open air.
- Waterpump; Waterpump function ensures the coolant keeps moving through the engine block, hoses and radiator, and maintains an optimum operating temperature.
- Water jacket; Water jacket is coolant tanks were covered the heat source inside the engine.
- Thermostat; Thermostat function is to open or closed the line of the coolant based on the temperature. If the coolant temperature is hot, then the thermostat valve will open so the coolant can flow to the radiator. If it's cooling down, then the valve will close the line.
- Waterpipe and bypass hoses; Waterpipe and bypass hoses are used to bypass the line between the radiator and the engine. It makes the coolant can circulate without waiting for the thermostat valves to open.
- Temperature gauge; Temperature gauge is used to giving information to the driver about coolant temperature.
- Engine coolant temperature sensor; Engine coolant temperature sensor is used by the engine control unit to measure the coolant temperature.
For a more detailed explanation of each component, you can read the Components of the car engine cooling system that we have posted in the previous post.
II. Diagram of the cooling system in a car
See the picture below for a diagram of the cooling system in a car before we learn how a car cooling system works.
III. Car cooling system works
This part will give you information about how car cooling systems work by coolant temperatures conditions such as cool temperature, ideal working temperature, overpressure, and under pressure. Here is the car cooling system works.
1. Cool temperature
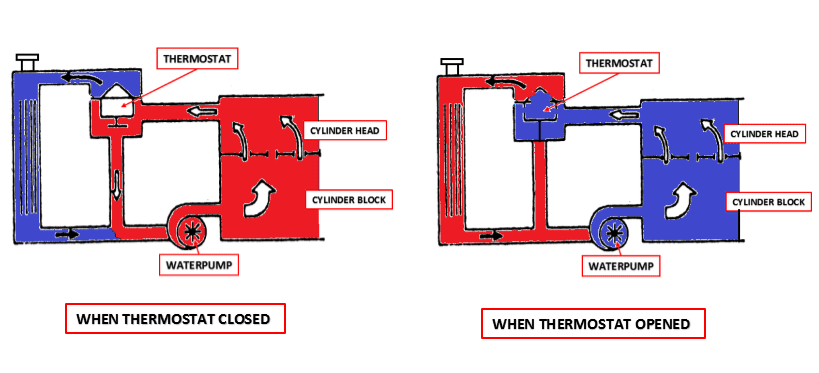
The temperature gauge can show the cool temperature if the pointer is pointing at the C (cool) mark. When in cool temperature, the coolant is circulating only inside the engine. The coolant flows through these parts.
Cylinder block water jacket > cylinder head water jacket > bypass hose > waterpipe > waterpump > back to cylinder block water jacket.
See the image below
When the coolant temperature is cool, the thermostat closes its valve, so the water pump pushing the coolant to circulate inside the engine only. With these conditions, the engine can raise its temperature quickly for efficient fuel usage and better performance.
2. Ideal working temperature
An ideal working temperature is an ideal temperature for the engine to works. It should be at 200 Fahrenheit or at least at 93 Celcius. At this temperature, the coolant circulation is inside the engine. Still, it also flows through the radiator and back to the engine after cooling down inside the radiator.
Cylinder block water jacket > cylinder head water jacket > thermostat> upper hose > radiator > lower hose > waterpump > back to cylinder block water jacket.
The thermostat holds an important function to the system. When the coolant temperature reaches the ideal working temperature, the thermostat valve will open the line, so the coolant can flow to the radiator to release its heat.
Meanwhile, the cooler coolant inside the radiator will be pushed away by the hot coolant to get into the engine and do its function to absorb the heat.
When the cooler coolant touches the thermostat valve, the valve slowly gets closed, and also it stops the flow of the coolant. So the coolant inside the engine can absorb the heat while the coolant inside the radiator can cool its temperature.
Here are the coolant flowing when the thermostat open and close
3. Overpressure and under pressure
Overpressure usually happens when the temperature gets high, while under pressure is in low temperature. In several cases, the coolant temperature has risen more than the ideal temperature to raise the coolant system pressure.
Suppose the pressure exceeds the radiator cap pressure. In that case, the coolant will flow to the reservoir tank, reducing the pressure inside the system. Reduced pressure makes the radiator cap pressure valve closed the line to the reservoir tank.
At low temperatures, the cooling system pressure has lower pressure than the atmospheric pressure. When the engine runs, it creates a vacuum condition inside the system. The vacuum condition pulls the vacuum valve inside the radiator cap, so it also pulls the coolant inside the reservoir tank.
The radiator cap controls the overpressure and underpressure inside the cooling system, so the pressure is always in stable conditions.